13: Holonyms, Synonyms, Antonyms, Taxonomy
LINGUISTICS ORGANIC SEARCH ENGINE THEORY
(LOSE-T) PART XIII
(LOSE-T) PART XIII
Search Engine Optimization (SEO), (SERP), (NLP), Holonyms, Synonyms, Antonyms, Taxonomy
In paper VI Search Engine Optimization (SEO), (SERP), (NLP), Paronyms, Hyponyms, Meronyms, Hypernyms, we explored a myriad of taxonomies, hence we’ll use paper VI as a reference point. Holonyms are the whole of a subset or smaller part, synonymous to meronyms being the subset of a whole part; holonyms are synonymous to hyponyms and hypernyms in terms of the former ascribes to smaller part of a larger classification, and the latter ascribes to the larger part of a smaller classification. Whereas holonyms deals with the whole part of a smaller subset.
Holonyms are classified in polar opposites to meronyms in that they deals with subsets to a larger whole. Examples, “fingers, and “toes,” are the meronyms of hands, and “feet,” and “hands, and “feet,” are the holonyms of “fingers,” and “toes.” Hyponyms and hypernyms are antonymous classifications; example, “fish,” is the hypernym of “salmon,” and “piano,” is the hyponym of “instruments.” Notice the different between the four classifications? Holonyms and meronyms is attributed to the “subset-whole,” relationship; whereas, hyponyms and hypernyms ascribe to the “small-large classification.”
Synonyms is the taxonomical relationship phrases or lexemes similar in meanings; example, hypernyms and holonyms are synonyms in the abstract sense because both concepts explicate the whole and broad scope of subsets and classifications. Example,” flower,” is the hypernyms of “tulips,” “daisy,” “roses,” and “hibiscus;” and “hands,” and “feet,” are the holonyms of “fingers,” and “toes.” The difference between the former and latter is the classifications vs the subsets, but they’re synonymous because they’re the superior order in both representations.
Synonyms are classified into dominant classifications because of its general use, and subordinate classifications because of its secondary usage. General words such as “smart,” being the generally used term may be the dominant synonym compared to terms such as “canny,” “and “astute;” although the latter terms have slightly different meanings they’re denotationally comparable. Remember synonyms are not contingent on exact parallels, a near relation is enough to constitute the association, and the most generally used terms of these classifications becomes the neutral dominance.
Whereas hyponyms and meronyms are synonymous in the conceptual sense because the former is the specifics of a broad scope or whole, and the latter is the subset of a whole or larger part. Example; “daisy,” “roses,” and “hibiscus,” are the hyponyms of “flowers,” and “fingers,” and “toes,” are the meronyms of “hands,” and “feet.” Notice the synonymity between hyponyms and meronyms? They’re synonymous because they’re the inferior order in both representations. Let’s explore these same concepts using antonymous representations.
Antonyms are the complete contrast or polar opposite of synonyms in that they’re semantically polarized in their denotation; I’ll use holonyms and meronyms as examples (AGAIN); “hands,” and “feet,” are the holonyms of “fingers,” and “toes,” and “fingers,” and “toes,” are the meronyms of “hands,” and “feet.” Hyponyms and hypernyms are antonymous because they’re contrasted in meanings; example “daisy,” “roses,” and “hibiscus,” are the hyponyms of “flowers,” and “flowers,” are the hypernyms of “daisy,” “roses,” and “hibiscus.” Synonymously speaking, “hyponyms-meronyms,” and “holonyms-hypernyms,” are related; antonymic-ally, “hyponyms-hypernyms,” and “holonyms-meronyms,” are related. These semantic definitions are paronyms because of their derivational and inflectional morphological relationships, hence the interchangeable use in syntax….
SYNONYMS
Hyponyms – (smaller part of a larger classification)
Meronyms – (the subset of a whole)
Hypernyms – ( larger classification of a smaller part)
Holonyms – (the whole of a subset)
ANTONYMS
Hyponyms – (smaller part of a larger classification)
Hypernyms – (larger classification of a smaller part)
Holonyms – (the whole of a subset)
Meronyms – (the subset of a whole)
PARONYMS
Hypo-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
Mero-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
Hyper-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
Holo-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
Hypo-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
Hyper-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
Holo-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
Mero-nyms – (derivational and inflectional morphemes)
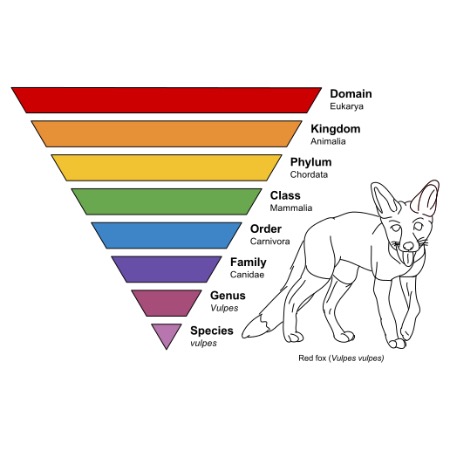
Taxonomy is a term prevalent in biology and used for the classification of organisms, organizing species based on similarities. You’ve probably seen taxonomic infographics depicting the arranged genus of different species. Taxonomy applies within the context of semantics and the subset of linguistics synonyms and antonyms pervades; this process classifies lexemes, figurative and rhetorical devices into their own species of taxonomy. One of the conundrum in Natural Language Process (NLP), is the Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD), and machines inability to unequivocally discern different sorts of ambiguity. Linguistics Organic Search Engine Theory (LOSE-T), demystifies ambiguity by curating the taxonomic aspect of semantics, phonology, grammar, punctuation, phonetics, morphology and syntax.
Holonyms, synonyms and antonyms are peculiar sorts of ambiguity, because they’re not predicated on the noun and verb disparity; phonological aspect of sound; punctuation to alter syntax, or grammatical functions. The functions represent associative meanings; example, “ubiquitous,” “prevalent,” “pervasive,” “pervade,” “propagate,” and “promulgate;” they’re either adjectives or verbs that share synonymous semantics. This is another kind of semantic ambiguity; the adjacent and proximity that induces vague distinctions; these devices explicate taxonomy the search query excludes from the curation, unless, it’s manually searched by someone studying literature.

INTRODUCTION TO (LOSE-T) THE EVOLUTION OF (LOSE-T) | THE HISTORY OF (LOSE-T) PHENOMENOLOGY (LOSE-T) |

Introduction To (LOSE-T) Search Query Disambiguation (SQD)
(1) (SEO), (SERP), (NLP), Derivational & Inflectional Morphology
(2) (SEO), (SERP), (NLP), Metaphor, Analogy, Metonym
(3) (SEO), (SERP), (NLP), Polysemy, Capitonym, Monosemy
(4) (SEO), (SERP), Homonym, Homophones, Homograph
(5) (SEO), (SERP), Segmental & Suprasegmental Phonology
(6) (SEO), (SERP), Paronym, Hyponym, Meronym, Hypernym
(7) (SEO), (SERP), Onomatopoeia, Denotation and Connotation
(8) (SEO), (SERP), Heteronym, Heterograph, Orthographic Units
(9) (SEO), (SERP), (NLP), Cuneiform, Pictographs, Ideographs
(10) (SEO), (SERP), Logographs, Hieroglyphics, Phonographs
(11) (SEO), (SERP), Abbreviations, Acronyms-Hybrids, Initialisms
(12) (SEO) (SERP) Anthropomorphic, Personification, Typography
(13) (SEO), (SERP) Holonyms, Synonyms, Antonyms, Taxonomy
(14) (SEO), (SERP) Prefix, Suffix, Affix, Infix, Circumfix, Morpheme
(15) (SEO), (LOSE-T) Taxonomic Framework To Encode (NLP)
(16) (SEO), (SERP) Absolute, Comparative, Superlative Adjectives
(17) (SEO), (SERP) Redshift, Doppler, Special & General Relativity
(18) (SEO), Possessive, Demonstrative, Indefinite Adjectives
(19) (SEO), (NLP), Proper Nouns, Common Nouns, Capitonymic
(20) (SEO), (NLP), Modulation, Cadence, Intonation, Inflection
(21) (SEO), (NLP), Terminology, Jargon, Verbosity, Slang/Ebonics
(22) (SEO), (NLP) Phonemes, Graphemes, Morphemes, Digraphs
(23) (SEO), (NLP), Autocomplete, Spelling Correction Predictions
(24) (SEO), (NLP), Algorithmic Paradoxes, Equilibriums, Axioms
(25) (SEO), (NLP), Chromatics, Diatonics, Logarithmics, Octaves
(26) (SEO), (NLP), Anaphora, Cataphora, Antecedent, Postcedent
(27) (SEO), (NLP), Hegelians Dialect; Thesis, Antithesis, Synthesis


(1) Fundamental vs Technical Analysis in The Stock-Market
(2) Predicting The Stock Market Using Dispersed Variables..
(3) (SEO), (SMO), (SERP), And Google Algorithms..
(4) ICANN), (gTLD), Domain Registras & Cyber-Squatting..
(5) Domain Names (gTLD), Effect On (SEO), Stock-Market..
(6) 10-K, 10-Q, Annual Reports And Google Revenue..
(7) (ICANN), (UDRP), Domain Trademark And Cybersquatting..
(8) Economic Correlation/Advertisement, Marketing & Commodity!

(1) Three Dimensional Paradoxes In Spatial Schemata
(2) Vibrating Molecules and Elliptical Bubbles
(3) Musical Octaves and Wave-Particle Duality
(4) Smells Velocity Induces Memory Faculty
(5) The Paradox of Light and Sound Induces Synesthesia
(6) The Trichotomy Between Amplitude, Frequency and Velocity
(7) Black Is An Electromagnetic-Radiation (EM) Paradox
(8) Quantum Field Theory, Nash Equilibrium & Social Science
(9) Quantum Electrodynamics, Intramolecular, Intermolecular
(10) The Fibonacci Sequence & Coriolis Effect; Music & Motion

(1) The Emotional Dichotomy in Humor
(2) Neuro-Behavioral Disorder Adaptation
(3) Why Comedians Don’t Laugh At Open Mics
(4) Economic Psychology and Humor Aberration
(5) The Philosophy And Psychology Behind Fozzie Bear Humor
(6) Women Comics! A Sociobiological and Economical Analysis
(7) The Trichotomy Between Instinct, Intuition and Improvisation
(8) Synasthesia, Psychophysics, Linguistics and Humor!


| Synchronicity, Serendipity, Irony, Coincidences | ||

(1) Ecological Factors and Physiological Attributes
(2) The Psychology of Politics Equatable Rhetorics
(3) Psychophysics, Polyrhythm, Arrangement and Composition
(4) Smells Velocity Induces Memory Faculty
(5) Cognitive Impairment/Weather Conditions/Placebo Effect
(6) The Social Equilibrium of Spirituality vs Superficiality
(7) Quantum Entanglement, Chameleon Effect and Coincidences
(8) Synthesis Deriving From A Medical Antithesis
(9) The Power of Analogy, A Peculiar Mnemonics
(10) A Metaphor In Physics To Induce Organic Sleep
(11) Karma The Spiritual Undertone In Cause and Effect
(12) Distinctions Between Verbal Irony and Verbal Sarcasm
(13) School District Negligence, A Butterfly a Effect Analogy
(14) Dogs Defecating Alignment With The Earths Magnetic Field
(15) Fundamental vs Technical Analysis in The Stock-Market
(16) A Conglomeration of Political Discrepancy
Share your views and opinion, please leave a comment below Written By: Atelston Fitzgerald Holder 1st
SCIENTIST | ACADEMIC WRITER | LECTURER
The Harlem Times Politics | Business | Economics | Entertainment
Ask A Newyorker Science | Economics | Business | Politics
News Blaze World News | Science | Business | Technology
Performance Artist: www.youtube.com/mrpregnant
Musical Composer: www.youtube.com/mrpregnantmusic
Feel free to contact me at: mrpregnant@aol.com
Copyright 2016
Latest posts by Atelston Fitzgerald Holder 1st (see all)
- A SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OF THE SACRED-GEOMETRIC NATURE OF SUPERHERO ANATOMY! - September 5, 2023
- A Mirrored Reflection Of The Tainted Human Expression - September 15, 2021
- The God Universe Non-Dualistic Dichotomy - September 12, 2021
- Consultation - April 30, 2019
- The Philosophy Of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Bipolar I Manic, Lysergic Acid, Psilocybin & Sensory Modalities - January 31, 2018